How does GPS work?
The Global Positioning System (GPS) is a system of American satellites in orbit above the Earth. By receiving their signals, your smartphone is able to determine your position in real time, whether or not it is connected to a telephone network or the internet (WiFi, 3G/4G, etc.).
However, GPS is only used to establish your location. For all other information, including maps for viewing your location and obtaining directions, you need to use a dedicated app, previously installed on your phone or available from the Play Store.
You will also need an internet connection at some point, to access the maps and download them.
For more accurate and faster positioning, CROSSCALL* smartphones feature two other types of geolocation in addition to GPS: the A-GPS** and GLONASS*** systems.
*For the TREKKER-S1, TREKKER-X2, TREKKER-M1 and TREKKER-M1 Core models.
*A-GPS (or Assisted-GPS) enhances GPS performance. It provides more accurate location data and speeds up the search for your position using an internet or 3G/4G network connection in areas with poor GPS signal (built-up urban areas, buildings, tunnels, etc.).
**GLONASS is the Russian satellite system, similar to the American GPS.
Each time you use the GPS
GPS with “online” maps
This type of app requires an active internet connection in order for all its services to be available to the user, but does not need setting up prior to outdoor use. The GPS positioning is coupled with information downloaded and updated in real time to better represent reality (i.e. traffic, route planners, etc.). Apps of this type include Google Maps, Tomtom and Mappy.
GPS with “offline” maps
These navigation systems do not require an active network connection to locate you on a map. However, the map of the place or region where you plan to travel needs to be downloaded before you set off. If you intend to go off the beaten track and are likely to need to check your route in an area without signal, you should opt for this solution. Maps.me, Orux Maps, Visorando, Peakhunter and ViewRanger are some apps of this type.
While GPS apps with online maps are ideal for driving directions, GPS that use “offline” maps are more suitable for your outdoor activities.
To help you understand the purpose and benefits of an “on-board” app, we have decided to show you how to use the GPS on your CROSSCALL smartphone using the ViewRanger app, by answering three questions:
– how do you record a track?
– how do you use it in offline mode?
– how do you import a map from your computer to the app?
Follow the guide*!
*Tests were carried out on a TREKKER-M1.
HOW TO RECORD A TRACK USING VIEWRANGER IN ONLINE MODE ?
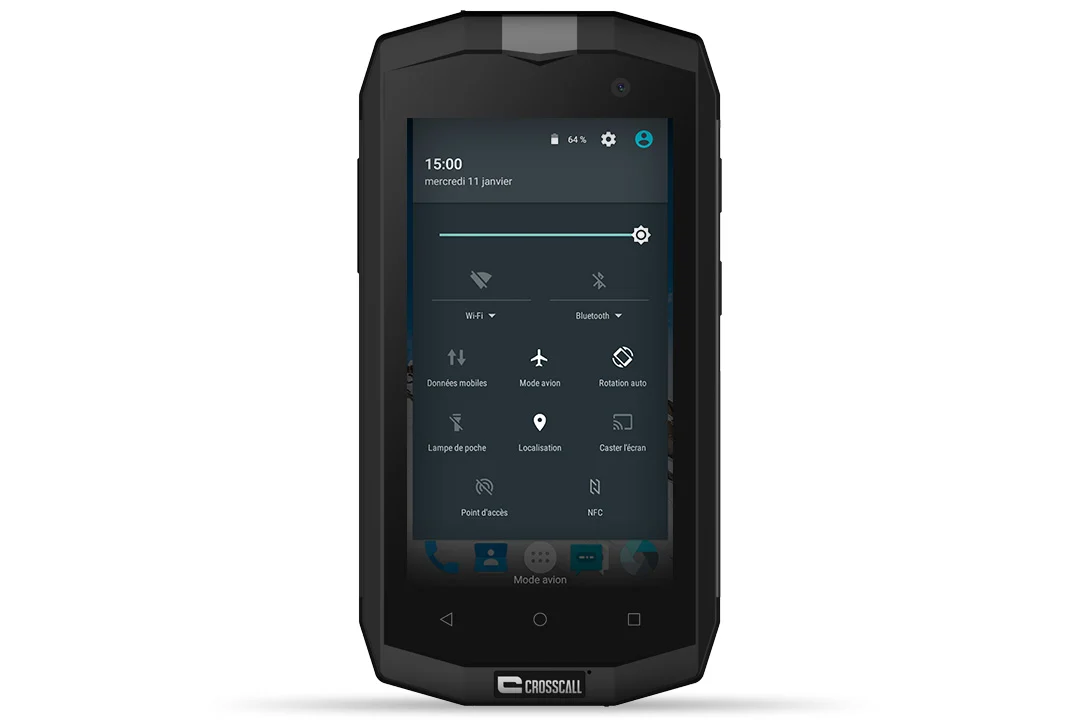
- Activate your smartphone’s GPS by “swiping” from the top to the bottom of your screen and selecting “Location” and “Mobile data” for better geolocation.
- Open the ViewRanger app, previously downloaded from the Play Store.
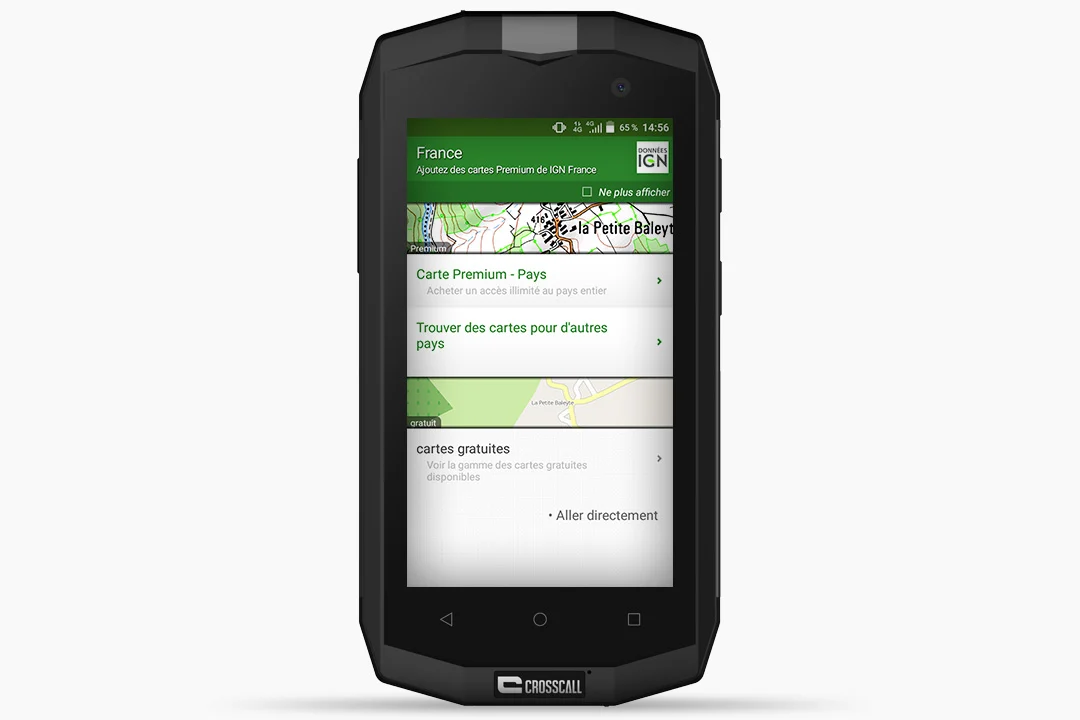
- The app provides you with access to both open source maps and premium maps (available with a subscription*). Select “Skip” to go straight to the free version.
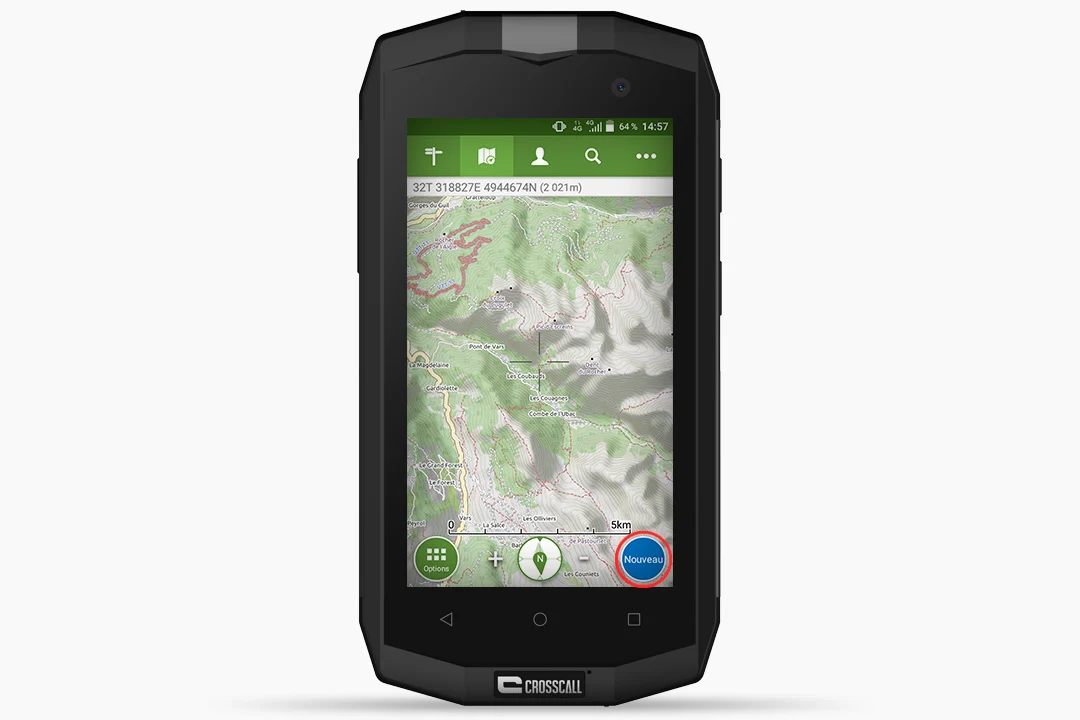
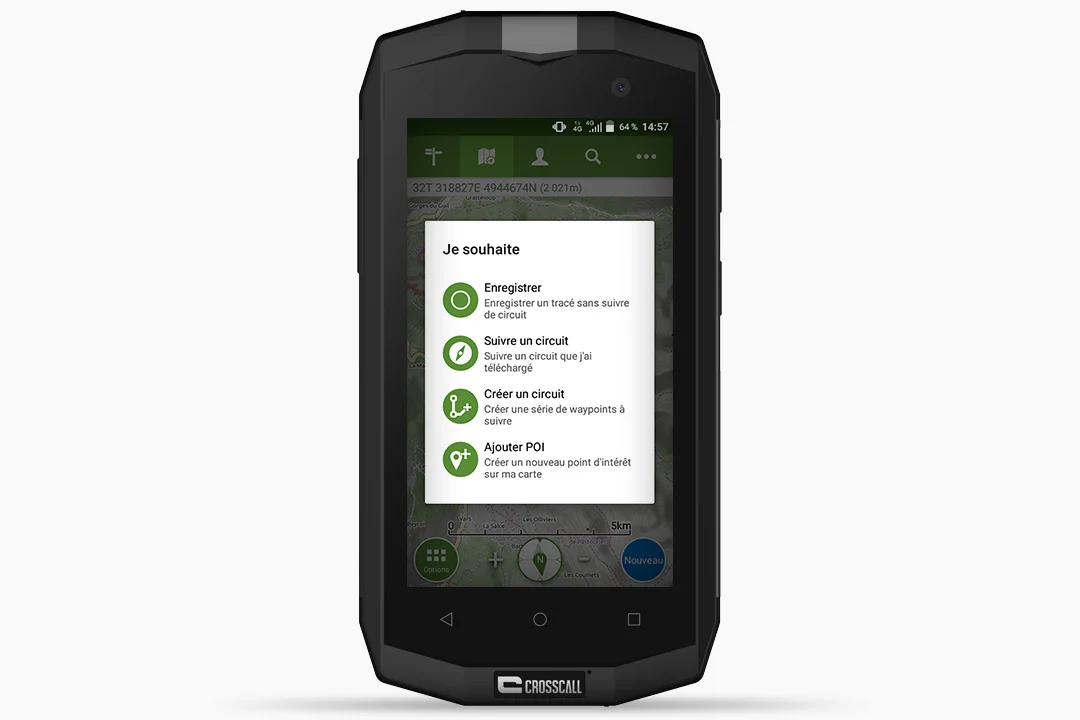
- Press the “New” button located at the bottom right of your screen.
- Several options appear. Select “Record track”.
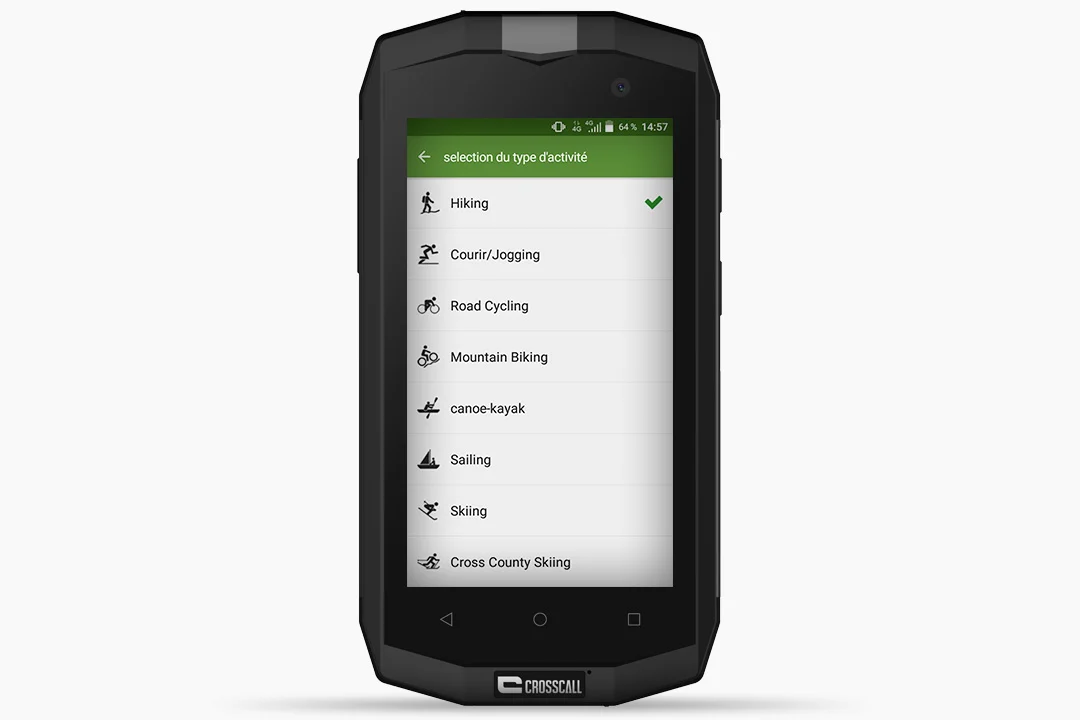
- Choose your activity type.
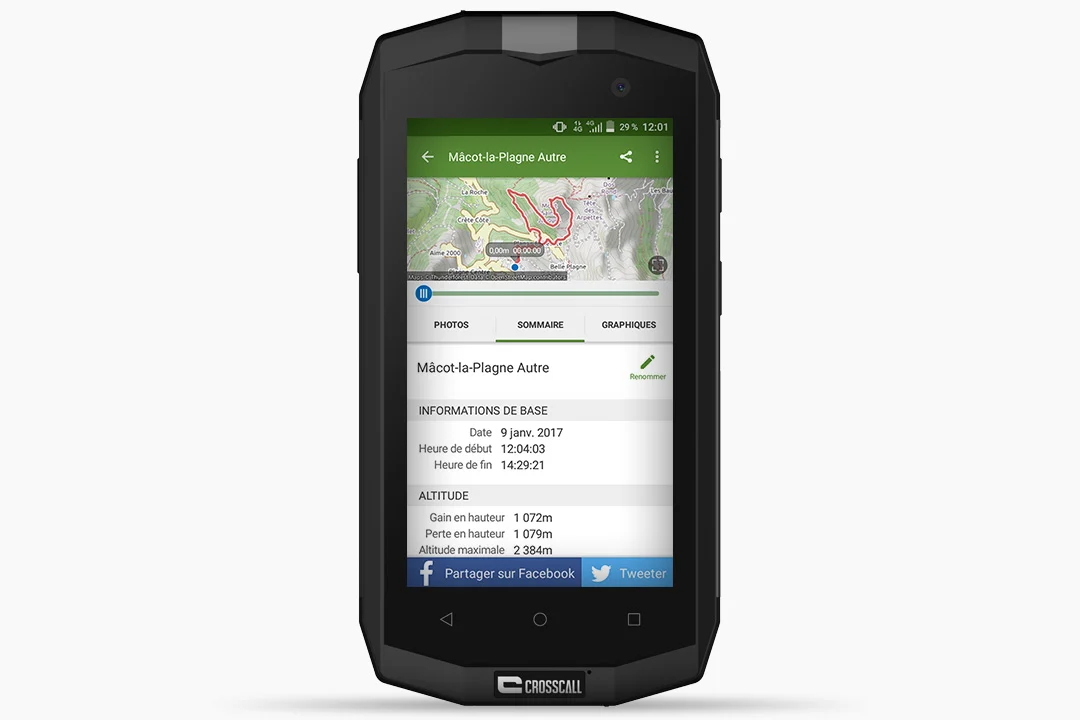
- Press the record button (red circle) to start tracking your route. You can pause the recording at any time by pressing and holding the record button. This means you can record the actual duration of your track without counting your stops.
- Next to the “Record” tab, the app gives you the real-time statistics of your trip such as trip distance, time, speed, average speed […].
- At the end of your outing, press the “stop” button (the square symbol located to the left of the record button). Wait a few seconds, and your track will be recorded.
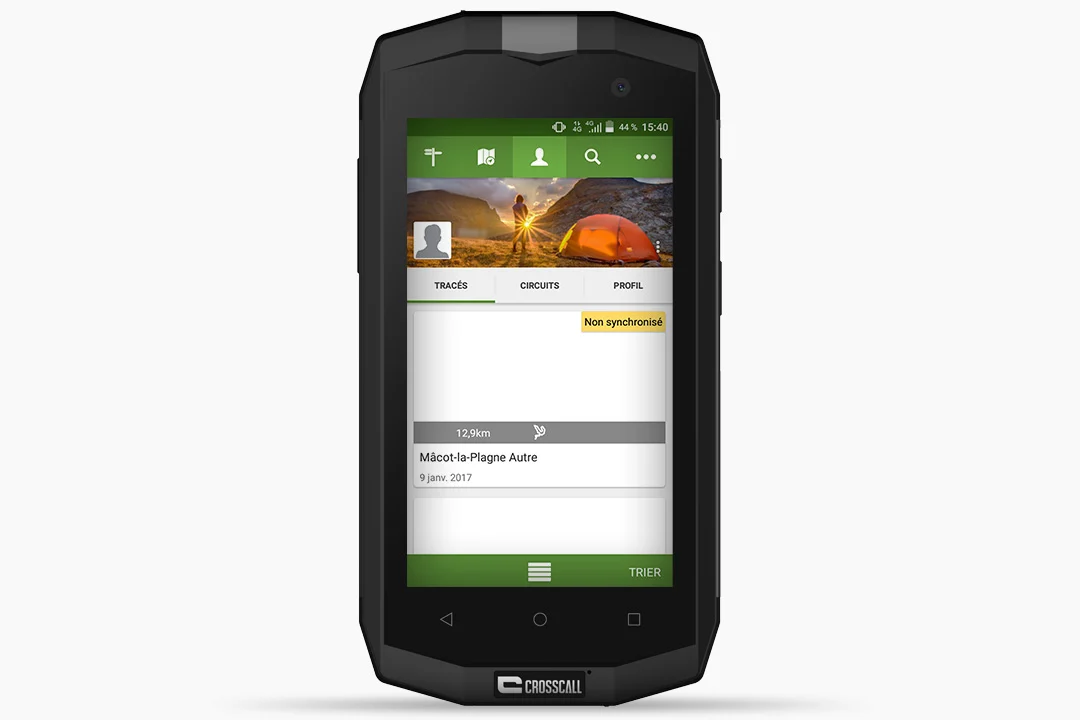
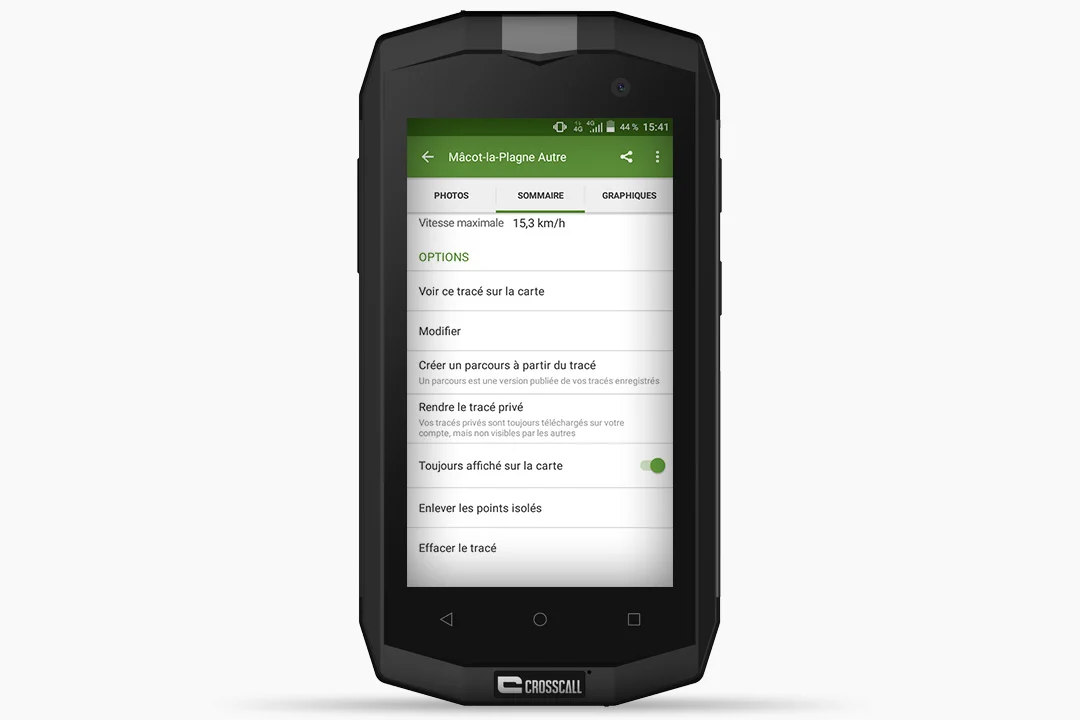
- Your route will then be saved on your “Profile” in the “TRACKS” tab. Then you can rename it, share it on Facebook and Twitter, see it displayed on a map, or create a new route based on your track.
*Subscriptions differ depending on the app.
HOW TO USE VIEWRANGER IN OFFLINE MODE ?
This method saves battery and allows you to view your location in areas with poor signal. To use it, you need to download the desired map via an internet connection.
- Open the ViewRanger app.
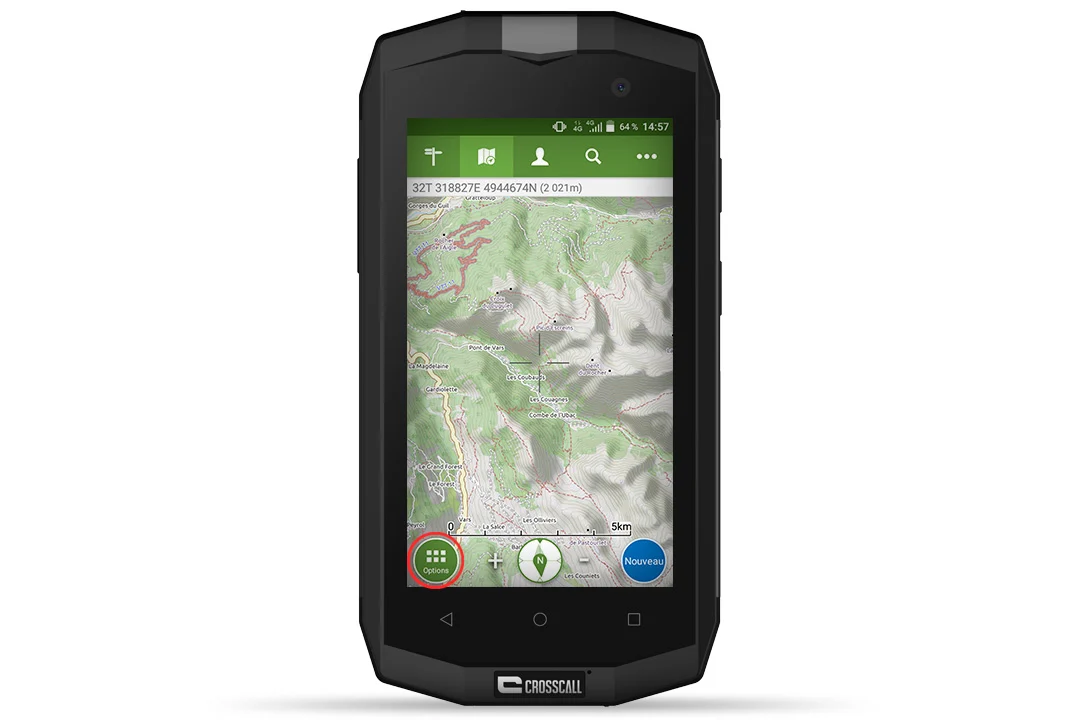
- Click the “Options” button located at the bottom left of your screen.
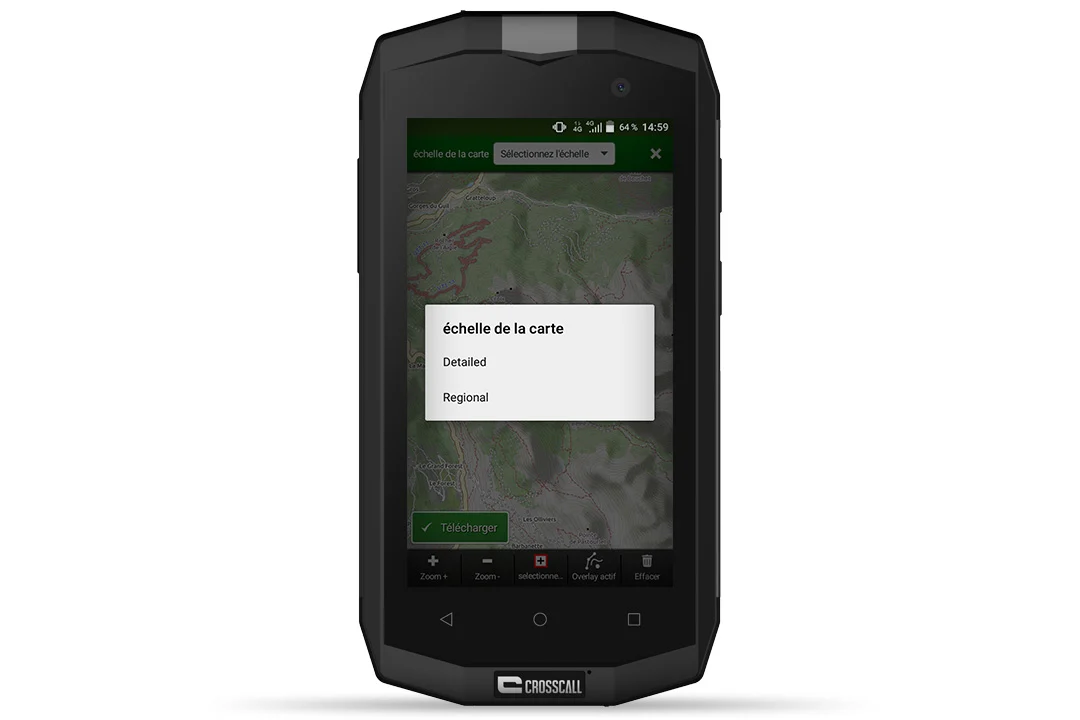
- Click on “Create saved map”.
- Decide whether you want the map scale to be “Detailed” or “Regional”. Some maps are open source and can be downloaded for free. More detailed Ordnance Survey maps (scale 1:25,000 or 1:100,000) are available with a subscription (€5.49 a month or €24.99 a year), for unlimited online access throughout France. It’s up to you to decide what best meets your needs.
- Then select the geographic area(s) (known as “tiles”) through which you intend to travel on your next trip by moving around the map. Press “Download”.
[Tip: when you press on “Select”, it becomes a “Move” button].
- Swipe from the top to the bottom of your screen. Enable “Flight mode “and “Location” for the GPS, then deselect “Mobile data”.
- Press the “Options” button again in ViewRanger, then “Select Map” and “My Maps” to choose from your saved maps.
- Follow the same steps as described above to record your next track or simply for geolocation purposes.
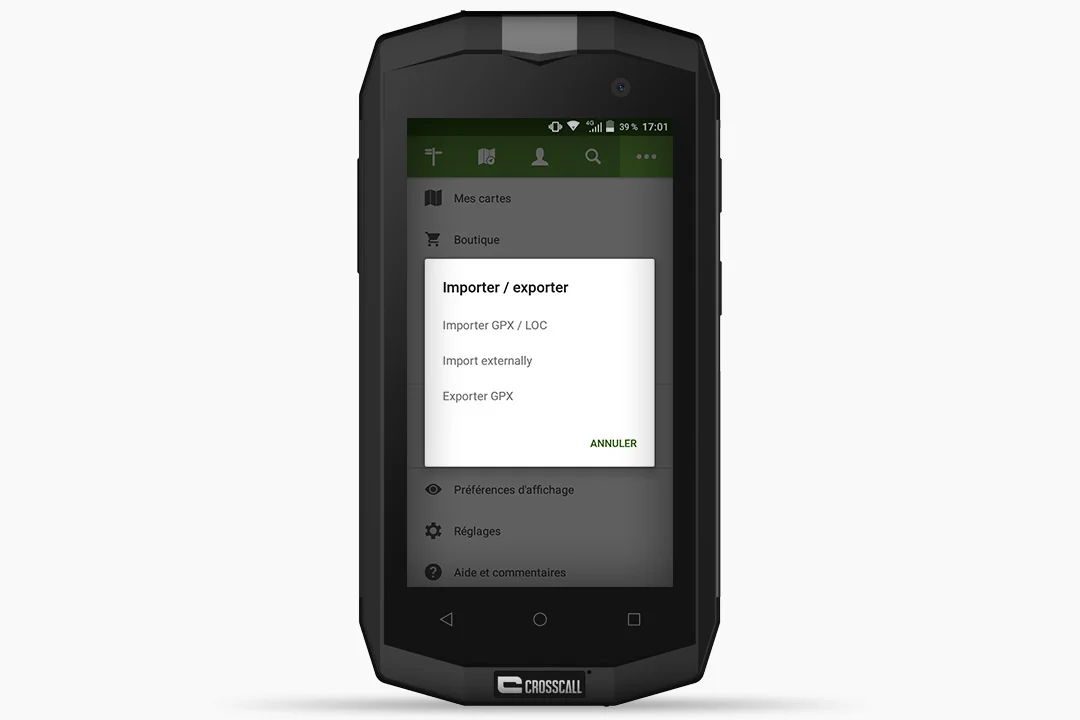
HOW TO IMPORT A MAP TO VIEWRANGER FROM YOUR COMPUTER ?
- Transfer your .gpx file from your computer to your phone via email, USB cable or SD card.
- Open the ViewRanger app.
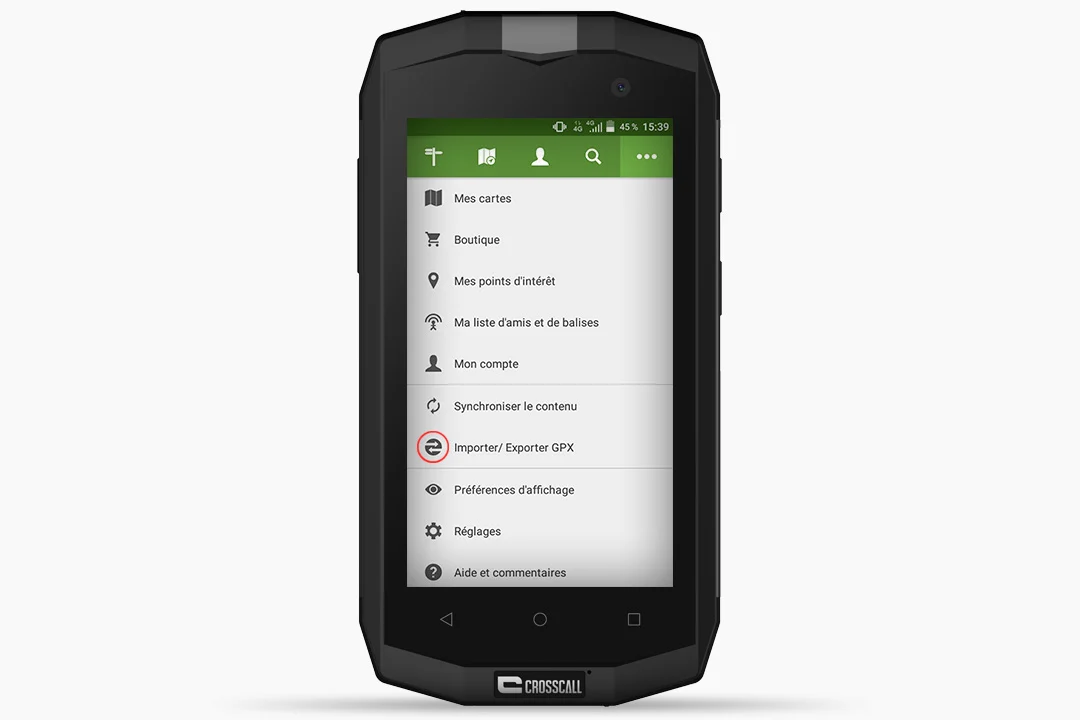
- Click on the “3 dots” (top right of the screen) and then on “Import/Export GPX”.
- For the purposes of this test, we imported a GPX track by email, chose to “Import Externally” and then selected the file from the phone’s “Download” folder.
- Return to your “Profile” on the app. In the “TRACKS” tab, it tells you that the map is “Not synchronized”.
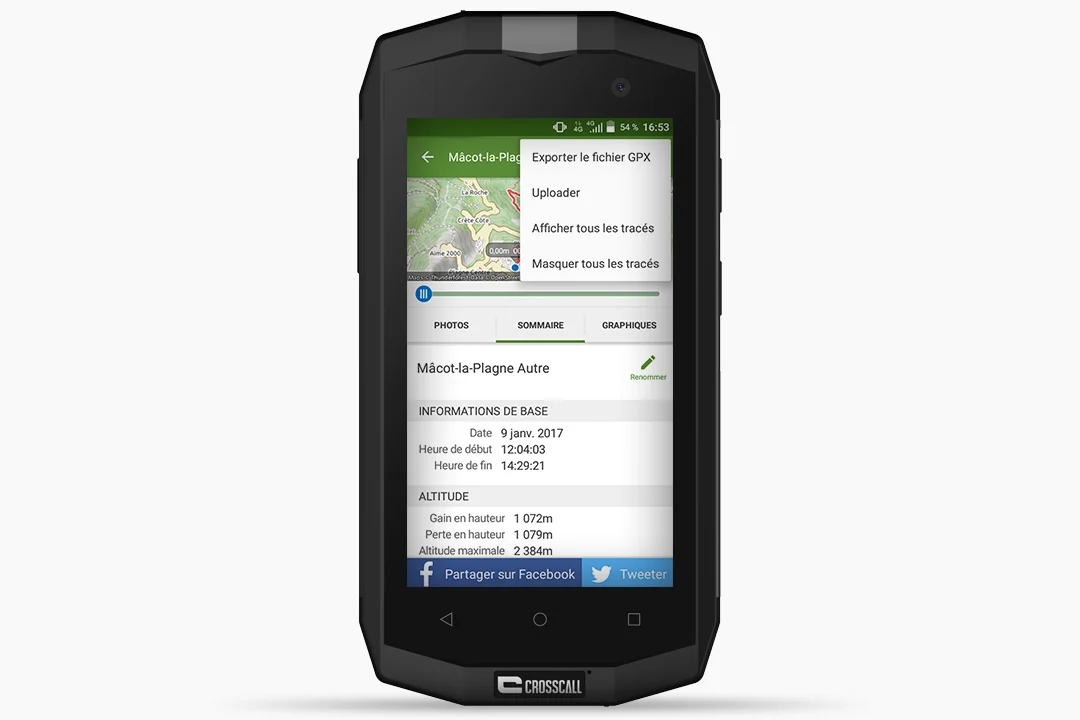
- Select the track, then click on the “3 dots” (top right) and finally on “Upload”. Your route is now synchronized.
- Still in the “TRACKS” tab, scroll down. Select “See this track on the map” to display or save your route based on the track, by choosing to create a “Route from track”.
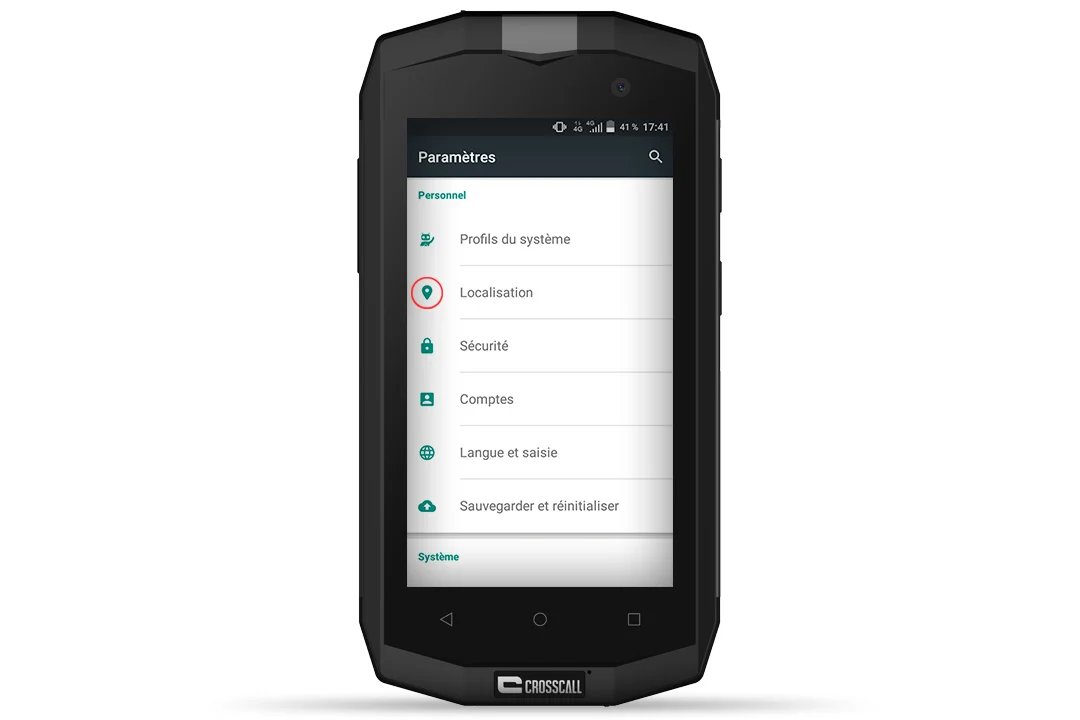
ANDROID TIP: IMPROVING THE ACCURACY OF YOUR GPS
- Go to the “Settings” of your smartphone.
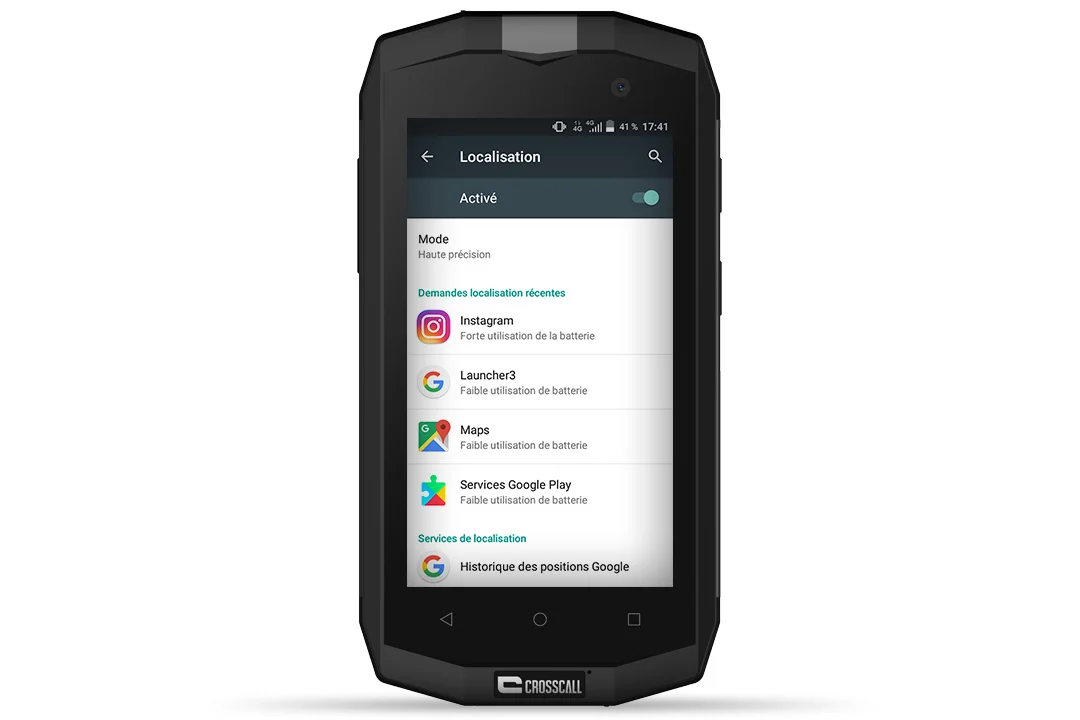
- Select “Location” and activate GPS mode.
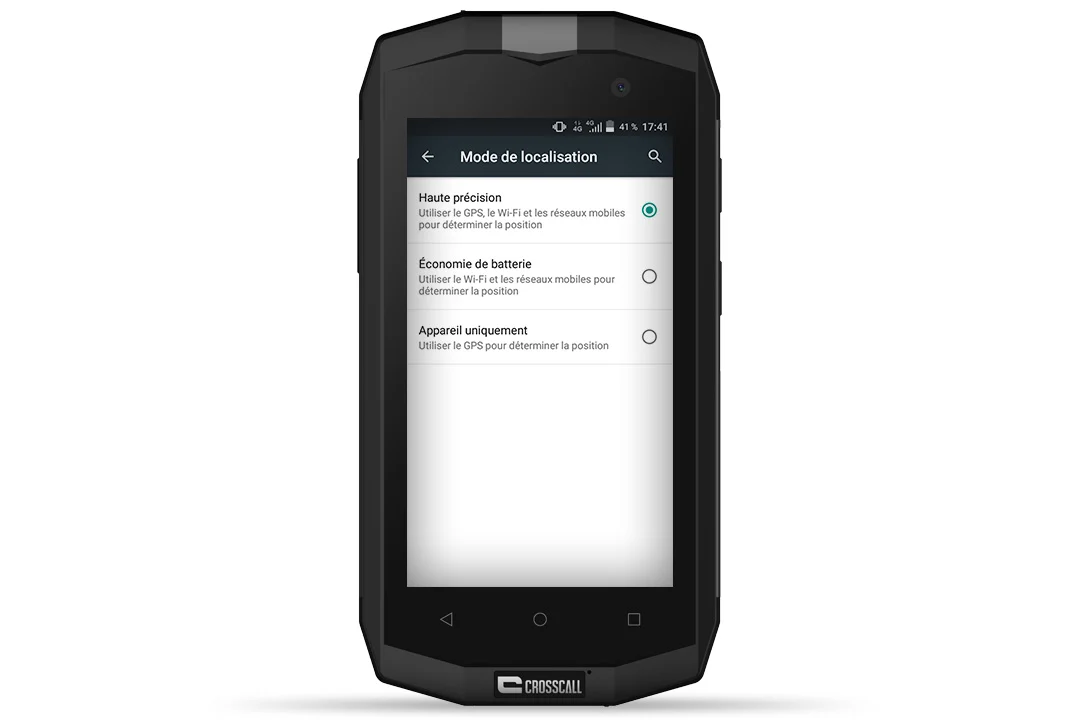
- Click on “Mode” then select the location mode as needed.
- 3 options are available:
- High accuracy. Here, GPS, WiFi and mobile data are all turned on to provide the best possible location accuracy. However, this method of location will mean high battery usage.
- Battery saving. This method calculates your position using WiFi networks. As its name suggests, it optimises the everyday battery life of your smartphone and still lets you use apps that work with geolocation (weather, social media, etc.) . However, this mode does not give you GPS accuracy during your outdoor excursions.
- Device only. Only the device’s GPS will be used to determine your position. By coupling it with flight mode, you won’t find a better option when it comes to battery life and saving on roaming charges. Very handy in areas with no signal, and when you need to find your way abroad!
 Choose your country and language
Choose your country and language